Data-driven VOC Analysis and Automated Dashboard Development: Reducing Cost and Maximizing Efficiency
“I learned that internal team members were facing difficulties in following up on Zendesk customer inquiries, so I developed a Redash VOC dashboard to address this issue. The system automatically collected and preprocessed Zendesk data, then used the OpenAI API to categorize and summarize customer inquiries by topic. Additionally, a Slack notification was set up to alert the team each Monday about the topics with the highest increase in inquiries, helping identify and respond to customer issues more efficiently. As a result, we were able to eliminate about $275 in opportunity costs each month and reduce the time spent by team members on VOC follow-ups.”
| Performance Summary |
|---|
- Opportunity Cost: $300/month → $25/month (92% ↓) |
Table of Contents
- STAR Summary
- Situation
- Tasks
- Actions
- Results
1. STAR Summary
Situation
- Internal team members were struggling to efficiently track and follow up on Zendesk customer inquiries. Reading through all the inquiries required an excessive amount of time and effort, and implementing an external VOC analysis service posed a cost burden.
Tasks
- I decided to categorize and summarize customer inquiries and create a Redash VOC dashboard.
- I also decided to build a Slack notification bot to alert the team about the most urgent customer inquiry topics.
Actions
-
Data Pipeline
1.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
(Zendesk Tickets → Google Sheets → BigQuery)1.2. Topic Categorization
(OpenAI API)1.3. Summarization
(OpenAI API) -
Dashboard and Notification Bot
2.1. Creating the Dashboard
(BigQuery → Redash)2.2. Building the Notification Bot
(BigQuery → Slack API)
Results
- Cost Savings
- We solved the problem internally at a cost of $25 per month, avoiding the need for an external service that would have cost $300 per month.
- Time Savings
- The time required for internal team members to follow up on VOC, identify issues, and respond was significantly reduced.
2. Situation
Internal team members were struggling to efficiently track and follow up on Zendesk customer inquiries. Reading through all the inquiries required an excessive amount of time and effort, and implementing an external VOC analysis service posed a cost burden.
Specific Situation
- It was taking too much time to follow up on dozens to hundreds of customer inquiries each week.
- It was challenging to identify which topics were negatively impacting the customer experience.
Feedback from Internal Team Members
- C-level 1: “I’m trying to stay on top of customer sentiment by regularly reading the inquiries, but there are just too many, and it’s very time-consuming.”
- C-level 2: “I’d like to introduce an external service for VOC analysis, but the cost is too high, so we’re hesitant.”
- CX Manager: “I want to share more VOC insights with colleagues and improve the speed of issue resolution.”
3. Tasks
- I decided to categorize and summarize customer inquiries and create a Redash VOC dashboard.
- I also decided to build a Slack notification bot to alert the team about the most urgent customer inquiry topics.

4. Actions
Data Pipeline
1.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
(Zendesk Tickets → Google Sheets → BigQuery)1.2. Topic Categorization
(OpenAI API)1.3. Summarization
(OpenAI API)Dashboard and Notification Bot
2.1. Creating the Dashboard
(BigQuery → Redash)2.2. Building the Notification Bot
(BigQuery → Slack API)
1. Data Pipeline
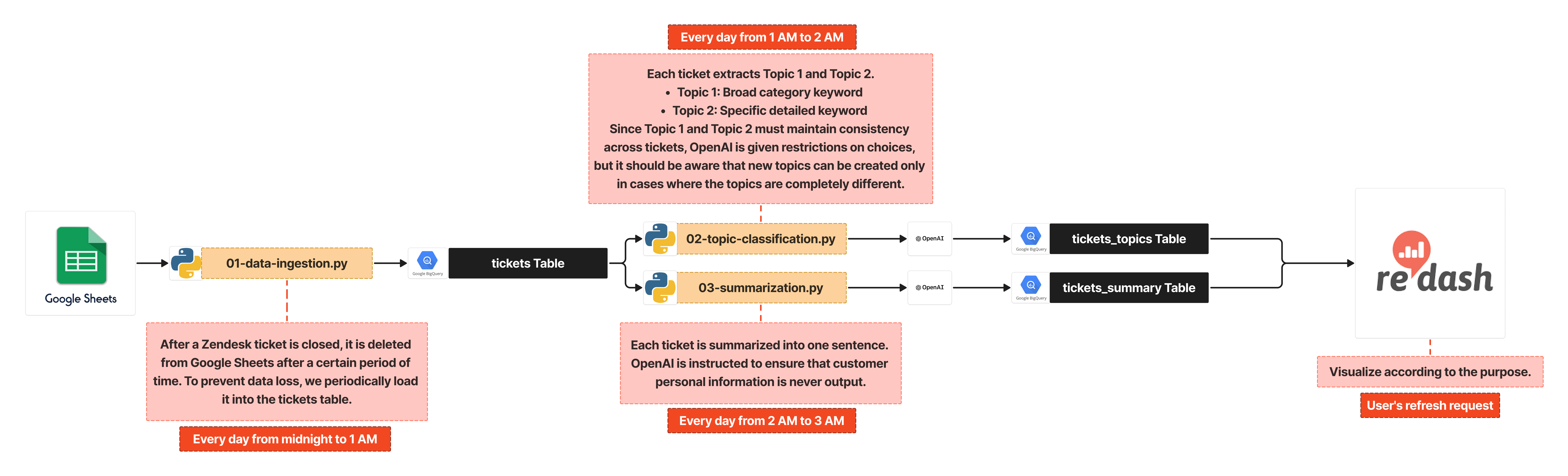
1.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing (Zendesk Tickets → Google Sheets → BigQuery)
1) First, I used the Zendesk Connector available from Google Workspace Marketplace to automatically store completed Zendesk ticket data in a private Google Sheet.

2) I then loaded the Google Sheets data into Python.
View Code
# Load Raw Data from Google Sheets (to `df`)
gc = gspread.service_account(google_sheets_credentials_fpath)
spreadsheet = gc.open_by_url(google_sheets_url)
sheet = spreadsheet.worksheet(google_sheets_worksheet_name)
sheet_data = sheet.get_all_records()
df = pd.DataFrame(sheet_data)
3) After that, I proceeded with data preprocessing.
Filter Only Necessary Columns
# Rename Columns
df = df.rename(
columns={
'created_at': 'created_datetime',
'raw_subject': 'subject',
'tags.0': 'zendesk_topic',
'updated_at': 'updated_datetime'
}
)
# Extract Only Necessary Columns
df = df[[
'id',
'created_datetime',
'zendesk_topic',
'subject',
'description'
]]
Change Timezone (UTC → KST)
# Convert Existing Timestamps: UTC to KST
kst = pytz.timezone('Asia/Seoul')
df['created_datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df['created_datetime'], utc=True).dt.tz_convert(kst).dt.tz_localize(None)
df = df.astype('str') # To load into BigQuery, all columns must be cast as strings.
Filter Only New Entries
# Remove Rows Already in Target Table (Prevent Duplicates)
query = f'SELECT DISTINCT id FROM `{bigquery_tickets_table_id}`'
try:
existing_ids = client.query(query).to_dataframe()
existing_ids = set(existing_ids['id'])
df = df[
~ df['id'].isin(existing_ids)
].reset_index(drop=True)
except:
df = df
4) Finally, I loaded the data into the BigQuery table.
View Code
# Load Data into BigQuery Table
table = client.get_table(bigquery_tickets_table_id)
client.load_table_from_dataframe(df, table)
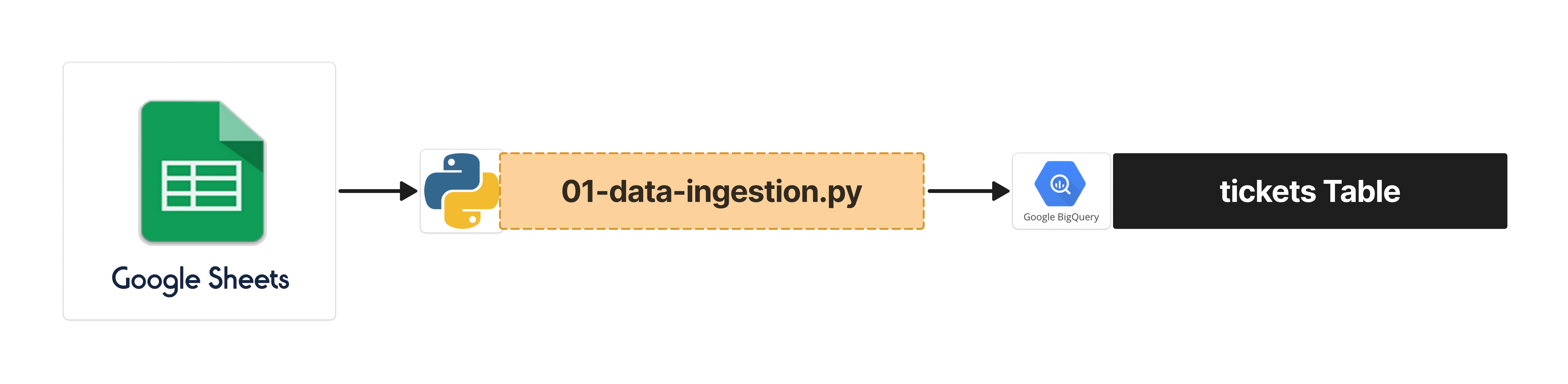
1.2. Topic Categorization (OpenAI API)
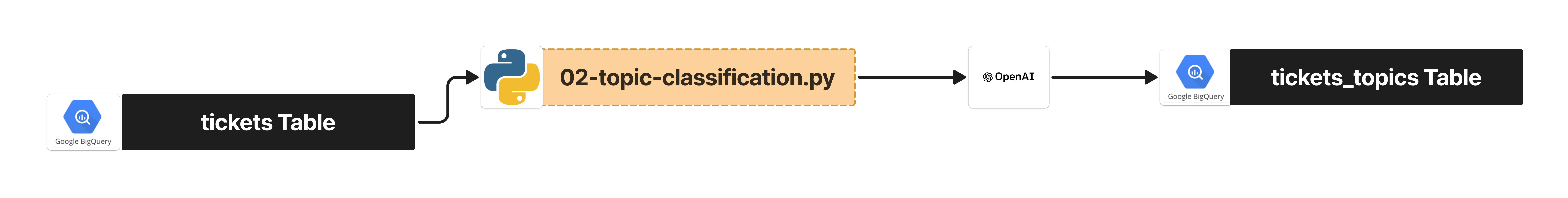
1) To predefine the list of topics to be categorized, I discussed and established a classification system with a CX manager and a UX/UI designer.
- Topic: Broad subject categories
- Keyword: Specific subtopics
2) I loaded the data from the BigQuery table into Python.
View Code
# Load BigQuery `tickets` Table (to `df`)
query = f'SELECT * FROM {bigquery_tickets_table_id}'
df = bigquery_client.query(query).to_dataframe()
3) I then filtered out only new entries.
View Code
# Remove Rows Already in Target Table (Prevent Duplicates)
query = f'SELECT DISTINCT id FROM `{bigquery_tickets_topics_table_id}`'
try:
existing_ids = bigquery_client.query(query).to_dataframe()
existing_ids = set(existing_ids['id'])
df = df[
~ df['id'].isin(existing_ids)
].reset_index(drop=True)
except:
df = df
4) I created the prompt to be sent to OpenAI.
System Prompt
Your task is to classify a single key keyword from the customer inquiry details. You must respond by selecting only from the provided list of topics. Below is the list of topics you can choose from:
{Keyword List}
Do not create or select any other topics.
User Prompt
Below is the customer inquiry details.
Extract a single key topic from this text.
Customer Inquiry Details:
{Actual Text}
Extraction Format: Topic
Restrictions:
1. Respond with only the topic.
2. Choose only from the provided list of topics. Do not create or select any other topics.
3. Make sure to select one from the list below:
{Keyword List}
Extraction Result:
5) I then obtained the main topic by calling the OpenAI API.
View Code
# Define the system prompt for OpenAI
prompt_system = f'''
Your task is to classify a single key keyword from the customer inquiry details. You must respond by selecting only from the provided list of topics. Below is the list of topics you can choose from:
{', '.join(topics2_list)}
Do not create or select any other topics.
'''
# Start the OpenAI API Request for each row
topic2_results_list = []
for i in range(len(df)):
# Subject + Description
text = df.loc[i, 'subject'] + ' ' + df.loc[i, 'description']
text = text[:2000] # Limit length to 2,000 characters (to save costs)
# Define the individual prompt for API Request
prompt_individual = f'''
Below is the customer inquiry details.
Extract a single key topic from this text.
Customer Inquiry Details:
{text}
Extraction Format: Topic
Restrictions:
1. Respond with only the topic.
2. Choose only from the provided list of topics. Do not create or select any other topics.
3. Make sure to select one from the list below:
{', '.join(topics2_list)}
Extraction Result:
'''
# Start the API Request
result = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model = 'gpt-4',
max_tokens = 500,
n = 1,
temperature = 0,
stop = None,
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": prompt_system},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt_individual}
]
)
# Record the topic results into Empty Lists
topic2_result = result.choices[0].message.content.replace('\'', '').replace('\"', '').replace('[', '').replace(']', '').strip()
topic2_results_list.append(topic2_result)
# Record the 'Topic 1' results using 'Topic 2' results
topic1_results_list = []
for topic2 in topic2_results_list:
for i in range(len(topics_list)):
if topics_list[i][1] == topic2:
topic1_results_list.append(topics_list[i][0])
break
if i == len(topics_list) - 1:
topic1_results_list.append('Others')
# Add 'Topic 1' and 'Topic 2' columns to the dataframe and select only the necessary columns
df['openai_topic_1'] = topic1_results_list
df['openai_topic_2'] = topic2_results_list
df = df[[
'id',
'created_datetime',
'openai_topic_1',
'openai_topic_2'
]]
6) Finally, the topic categorization results were loaded into a BigQuery table.
View Code
# Load Data into BigQuery Table
table = bigquery_client.get_table(bigquery_tickets_topics_table_id)
bigquery_client.load_table_from_dataframe(df, table)
1.3. Summarization (OpenAI API)
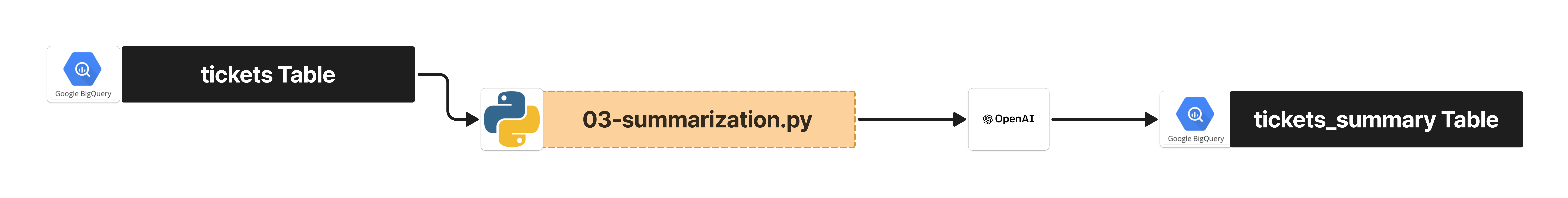
1) I loaded the data from the BigQuery table into Python.
View Code
# Load BigQuery `tickets` Table (to `df`)
query = f'SELECT * FROM {bigquery_tickets_table_id}'
df = bigquery_client.query(query).to_dataframe()
2) I then filtered out only new entries.
View Code
# Remove Rows Already in Target Table (Prevent Duplicates)
query = f'SELECT DISTINCT id FROM `{bigquery_tickets_summary_table_id}`'
try:
existing_ids = bigquery_client.query(query).to_dataframe()
existing_ids = set(existing_ids['id'])
df = df[
~ df['id'].isin(existing_ids)
].reset_index(drop=True)
except:
df = df
3) I created the prompt to be sent to OpenAI.
System Prompt
our task is to summarize customer inquiry details into a single sentence in Korean.
Keep in mind that the customer is from a blockchain hardware and app wallet service company.
The summary must be provided in a single sentence in Korean, and sensitive personal information or links must be removed.
User Prompt
Below is a customer inquiry.
Summarize this text into a single sentence in Korean.
Customer inquiry:
{text}
Format of extraction: One sentence in Korean
Constraints:
1. Remember that the customer is from a blockchain hardware and app wallet service company.
2. Summarize in Korean only. (However, proper nouns that cannot be translated may remain in English.)
3. Respond in only one sentence.
4. Ensure that sensitive personal information is removed. (e.g., personal details, wallet addresses, contact information, passwords, private keys, mnemonic phrases, email addresses, IP addresses, URLs, social media accounts, etc.)
Extraction result:
4) I performed the OpenAI summarization task by iterating over each ticket.
View Code
# Define the system prompt for OpenAI
prompt_system = '''
our task is to summarize customer inquiry details into a single sentence in Korean.
Keep in mind that the customer is from a blockchain hardware and app wallet service company.
The summary must be provided in a single sentence in Korean, and sensitive personal information or links must be removed.
'''
# Start the OpenAI API Request for each row
summaries_list = []
for i in range(len(df)):
# Subject + Description
text = df.loc[i, 'subject'] + ' ' + df.loc[i, 'description']
text = text[:2000] # Limit length to 2,000 characters (to save costs)
# Define the individual prompt for API Request
prompt_individual = f'''
Below is a customer inquiry.
Summarize this text into a single sentence in Korean.
Customer inquiry:
{text}
Format of extraction: One sentence in Korean
Constraints:
1. Remember that the customer is from a blockchain hardware and app wallet service company.
2. Summarize in Korean only. (However, proper nouns that cannot be translated may remain in English.)
3. Respond in only one sentence.
4. Ensure that sensitive personal information is removed. (e.g., personal details, wallet addresses, contact information, passwords, private keys, mnemonic phrases, email addresses, IP addresses, URLs, social media accounts, etc.)
Extraction result:
'''
# Start the API Request
result = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model = 'gpt-4',
max_tokens = 200,
n = 1,
temperature = 0,
stop = None,
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": prompt_system},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt_individual}
]
)
# Record the topic results into empty lists
summary_result = result.choices[0].message.content.replace('\'', '').replace('\"', '').replace('[', '').replace(']', '').strip()
summaries_list.append(summary_result)
# Add the summary column to the dataframe and select only the required columns
df['openai_summary'] = summaries_list
df = df[[
'id',
'created_datetime',
'openai_summary'
]]
5) Finally, the summarized results were loaded into a BigQuery table.
View Code
# Load Data into BigQuery Table
table = bigquery_client.get_table(bigquery_tickets_summary_table_id)
bigquery_client.load_table_from_dataframe(df, table)
2. Dashboard and Notification Bot
2.1. Creating the Dashboard (BigQuery → Redash)
1) I created a Redash dashboard with the following contents.
Proportion by Topic
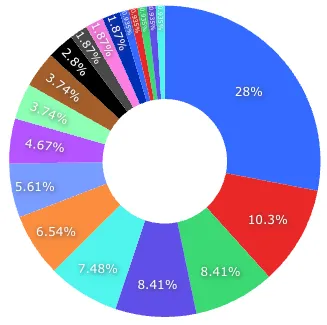
Trends by Topic

Trends by Keyword
Summary of Inquiries by Keyword
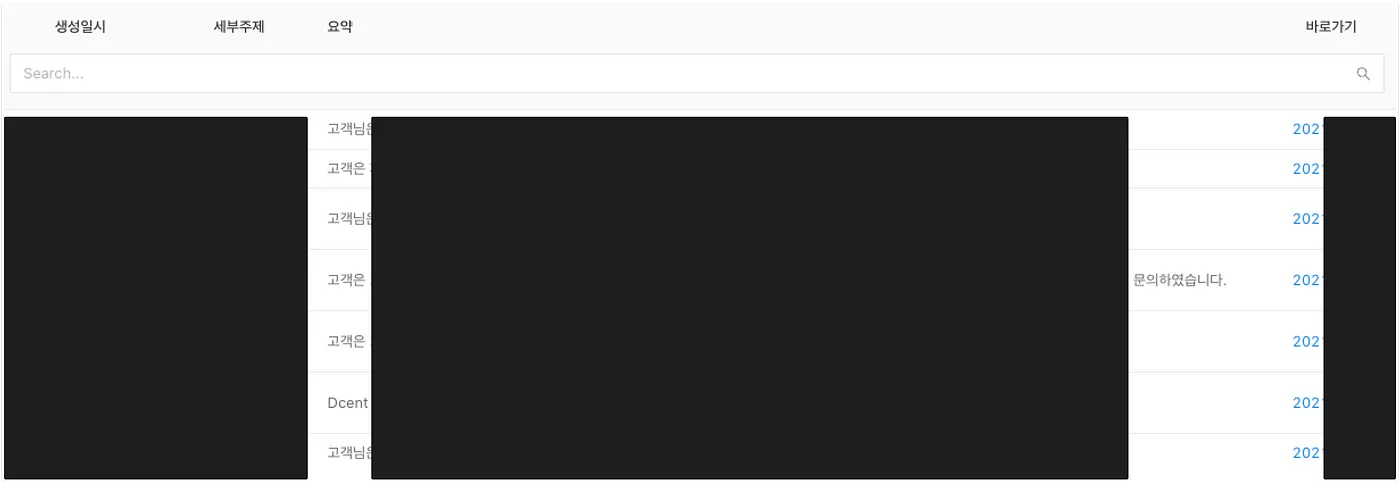
All Datasets

2.2. Building the Notification Bot (BigQuery → Slack API)
1) First, I wrote a BigQuery query.
Extracting the detailed topics (Keywords) with the most significant increase in customer inquiries from the previous week (compared to the week before)
WITH
CTE_1w_ago_raw AS (
SELECT
openai_topic_2,
COUNT(DISTINCT id) AS tickets_cnt
FROM
`bigquery_tickets_topics_table_id`
WHERE
DATE_TRUNC(DATE_ADD(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL -1 WEEK), WEEK) <= DATE(created_datetime)
AND DATE(created_datetime) < DATE_TRUNC(CURRENT_DATE(), WEEK)
AND openai_topic_1 != 'Others'
GROUP BY
1
),
CTE_2w_ago_raw AS (
SELECT
openai_topic_2,
COUNT(DISTINCT id) AS tickets_cnt
FROM
`bigquery_tickets_topics_table_id`
WHERE
DATE_TRUNC(DATE_ADD(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL -2 WEEK), WEEK) <= DATE(created_datetime)
AND DATE(created_datetime) < DATE_TRUNC(DATE_ADD(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL -1 WEEK), WEEK)
AND openai_topic_1 != 'Others'
GROUP BY
1
),
CTE_diff AS (
SELECT
COALESCE(MAIN.openai_topic_2, COMP.openai_topic_2) AS openai_topic_2,
MAIN.tickets_cnt AS tickets_cnt_1w_ago,
COALESCE(COMP.tickets_cnt, 0) AS tickets_cnt_2w_ago,
COALESCE(MAIN.tickets_cnt - COMP.tickets_cnt, 0) AS tickets_cnt_diff
FROM
CTE_1w_ago_raw MAIN
LEFT JOIN
CTE_2w_ago_raw COMP
ON MAIN.openai_topic_2 = COMP.openai_topic_2
)
SELECT
openai_topic_2,
tickets_cnt_1w_ago,
tickets_cnt_2w_ago,
tickets_cnt_diff
FROM
CTE_diff
WHERE
tickets_cnt_diff = (SELECT MAX(tickets_cnt_diff) FROM CTE_diff)
AND tickets_cnt_diff > 0
ORDER BY
1
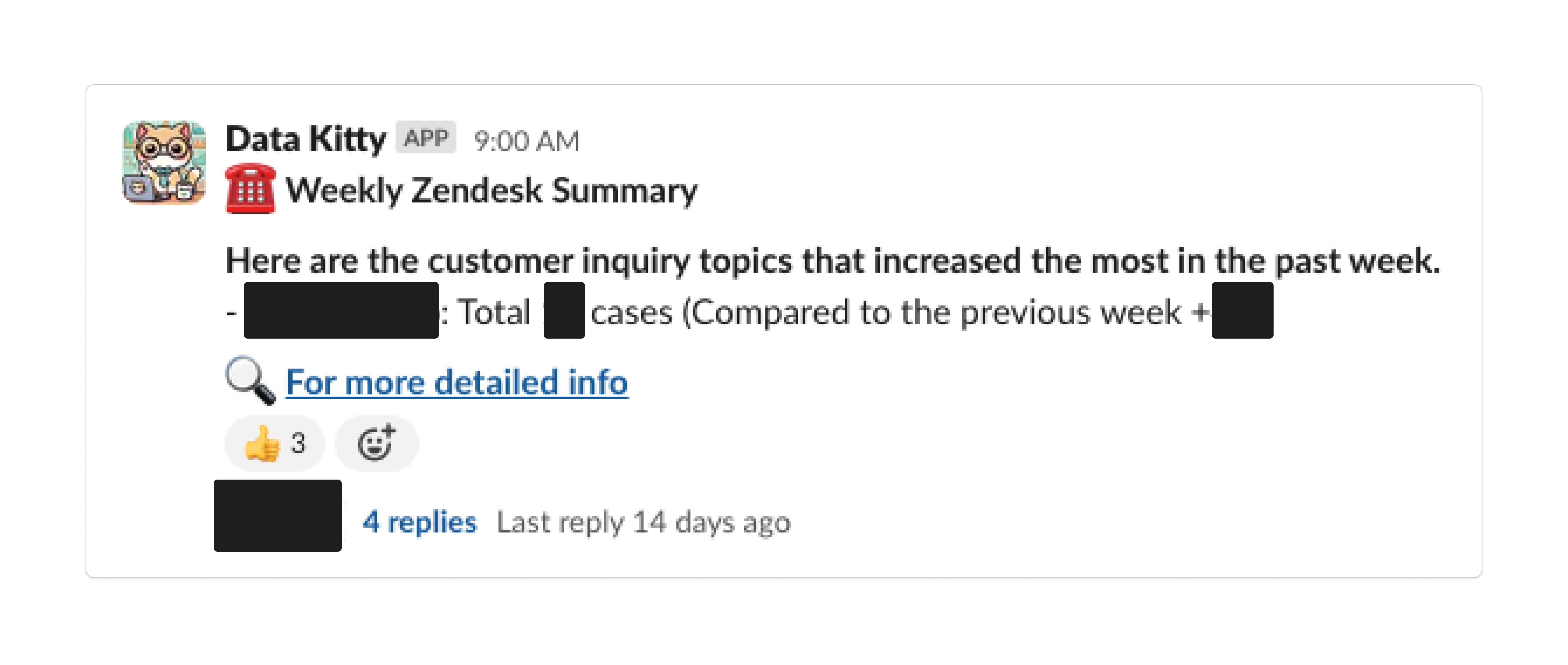
2) I created a Slack message object.
View Code
df = bigquery_client.query(query).to_dataframe()
# Slack Message Title
message = f':phone: *Weekly Zendesk Summary* \n\n'
message += f'*Here are the customer inquiry topics that increased the most in the past week.* \n'
# If data exists
if len(df) > 0:
topics = df['openai_topic_2'].tolist()
tickets_cnt_1w_agos = df['tickets_cnt_1w_ago'].tolist()
tickets_cnt_diffs = df['tickets_cnt_diff'].tolist()
# Create Slack message
for i, topic in enumerate(topics):
message += f'- *{topic}*: Total {tickets_cnt_1w_agos[i]} cases (Compared to the previous week +{tickets_cnt_diffs[i]}) \n'
# If no data exists
else:
message += f'- *There are no topics that increased.*:smile: \n\n'
3) Every Monday at 9:00 AM, the following Slack notification was sent.
5. Results
- Cost Savings
- We solved the problem internally at a cost of $25 per month, avoiding the need for an external service that would have cost $300 per month.
- Time Savings
- The time required for internal team members to follow up on VOC, identify issues, and respond was significantly reduced.
1. Cost Savings
Conclusion) By developing internally, we were able to eliminate approximately $275 in opportunity costs each month.
| External VOC Analysis Service | Internal Development | |
| Monthly Cost | $300 |
$25 |
1) External VOC Analysis Service
- The syncly service we considered adopting required a minimum monthly cost of $299.

2) Internal Development
- However, internal development required the following costs:
| Resource | Monthly Cost |
| 1. OpenAI API | $25 |
| 2. BigQuery Storage | Minimal |
| 3. BigQuery Query Usage | Negligible |
| 4. VM Instance Operation | Minimal, as we used existing instances |
| TOTAL | $25 + e |
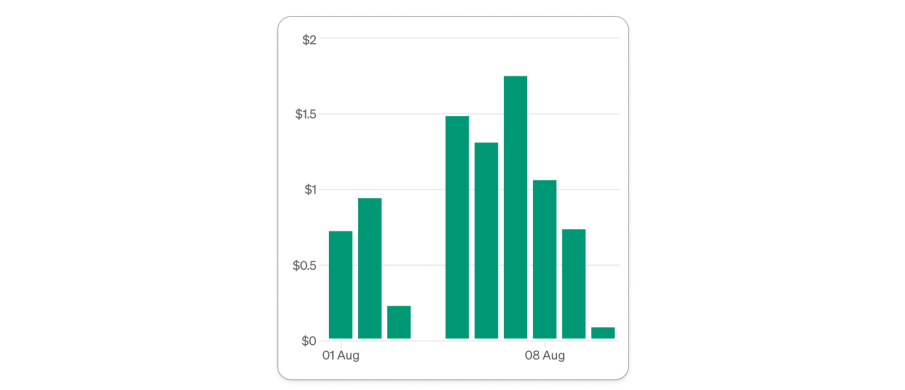
Daily OpenAI API Costs
2. Time Savings
1) Redash VOC Dashboard (Topic Categorization)
- Improved the ease of identifying VOC issues for internal team members.
2) Redash VOC Dashboard (Summarization)
- Enhanced the follow-up speed on VOC and improved accessibility for internal team members.
3) Slack Notification Bot
- Improved issue identification and response speed by sharing the topics with the highest increase in inquiries with internal team members each week, contributing to a shared understanding of the context.
Published by Joshua Kim
